Publications
Journal Articles
2025
85 A Streamlined Chemoenzymatic One-Pot Process for the Enantioselective Total Synthesis of Tenuipesone A/B
M. Hallamaa, A. O'Connell, J. Björklund, J. Deska, ChemRxiv, 2025, 10.26434/chemrxiv-2025-rbj31

Biocatalysis is a branch of catalysis that has allowed the development of a diverse range of sophisticated synthetic methodologies that target geometrically demanding structures such as pharmaceuticals, natural products, and their analogues. The routes are often more efficient due to enzymes innately high degree of chemo-, regio- and stereoselectivity, while making the overall process more sustainable when compared to their chemical equivalent, as enzymes are naturally biodegradable and operate under physiological conditions. Herein, we demonstrate the power of this catalytic approach via the development of a chemoenzymatic one-pot process that allowed access to the fungal metabolites tenuipesones A and B, along with their enantiomeric counterparts, in good yields (60-72 %) and excellent enantioselectivity (>99 % ee). The stereochemical outcome of the products was controlled through careful selection of the biocatalysts, enabling control of the configuration of the key C7 chiral center. This novel chemoenzymatic cascade process allowed access to all four possible stereoisomers, with their absolute stereochemistry being evaluated to confirm the true configuration of the natural isolates.
84 Rieske Oxygenase-Catalyzed Biotransformations in Recombinant Cupriavidus necator Fueled by Formate Oxidation
M. Hallamaa, H. P. F. Meier, M. Vajente, M. Ghirardi, J. Deska, S. Schmidt, ChemBioChem, 2025, e202500722 OPEN ACCESS
The use of single carbon (C1) molecules, such as carbon dioxide or formate, is crucial in the transition from a linear, petroleum-based economy to a circular bioeconomy. Formate can serve as both a carbon and energy source, further enhancing its attractiveness as a feedstock. Cupriavidus necator, a lithoautotrophic microbial chassis strain, provides an opportunity to leverage formate for the synthesis of valuable products. However, its ability to grow on formate and the subsequent coupling of that process to recombinantly produced redox enzymes for the efficient production of high-value-added products in a biotransformation has not yet been established. Here, we report the development of a formate-driven C. necator whole-cell chassis that recombinantly produces Rieske

(ROs) and elaborate on possible stress responses of the cells during formatotrophic cultivation. Our whole-cell chassis efficiently catalyzes the oxyfunctionalization of olefins fueled by formate oxidation. For instance, styrene was dihydroxylated to (R)-1-phenylethane-1,2-diol in an excellent 95 % yield and with good enantioselectivity (74 % ee) under formatotrophic conditions. The product yield and optical purity obtained demonstrate the synthetic usefulness of formate-fueled whole-cell biotransformations in C. necator.
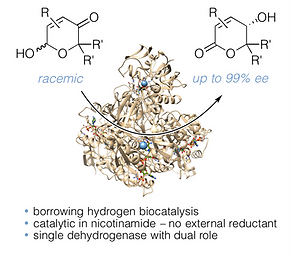
83 Asymmetric Ring Contraction of 2-Hydroxypyranones by Borrowing Hydrogen Biocatalysis
Y.-C. Liu, J. D. Rolfes, J. Deska, Chem. Sci. 2025, 16, 17667-17674 OPEN ACCESS
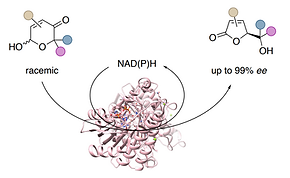
Ring contraction reactions facilitate easy access to carbo- and heterocyclic scaffolds from readily available precursors and have therefore enjoyed great popularity as a strategy in organic synthesis for a long time. By repurposing commercial alcohol dehydrogenases as borrowing hydrogen biocatalysts, we were able to develop a rare example of an enzymatic ring contraction methodology, where racemic 2-hydroxypyranones can be converted in an enantioconvergent manner to the corresponding 5-membered butenolides. The redox self-sufficient transformation delivers gamma-lactones in excellent optical purities and was successfully employed in the total synthesis of an Osmunda metabolite. Moreover, the biocatalytic tool was incorporated into a multi-step cascade consisting of six enzymes, achieving the formal enantioselective dearomatization of a furfuryl alcohol to deliver the corresponding saturated gamma-lactone in >99% ee.
82 Formaldehyde and Its Surrogates as C1 Platform for Defossilised Modern Societies
A. Rodil García, J. Deska, M. H. G. Prechtl, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2025, accepted
This tutorial serves as an accessible introduction for researchers and students interested in the multifaceted chemistry of formaldehyde and its potential in shaping a more sustainable future. We explore its roles in renewable energy storage in form of liquid organic hydrogen carriers (LOHCs) and renewable fuels, as well as carbon capture, utilization and storage (CCUS), and biomass valorisation. Furthermore, the relevance of these applications to several United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (UNSDGs 6, 7, 9, 12, and 13) is examined. Beyond the energy and environmental aspects, we discuss the use of formaldehyde and related surrogates in synthetic chemistry, focusing on innovative catalytic strategies to make use of this versatile and abundant C1 building block. Given formaldehyde’s central role as an intermediate in both synthetic and biological C1-H2 reaction networks, the tutorial additionally offers discussion points on related small molecules, including methane, methanol, formic acid, CO, and CO2
81 Guanidium Unmasked: Repurposing Common Amide Coupling Reagents for the Synthesis of Pentasubstituted Guanidine Bases
J.A.S. Aho, J.K. Mannisto, S.P.M. Mattila, M. Hallamaa, J. Deska, J. Org. Chem., 2025, 90, 2636-2643 OPEN ACCESS
Guanidines make up a class of compounds with important applications in catalysis and medicinal chemistry. In this systematic study, we report on the guanylation of aliphatic amines, anilines, (sulfon)amides, ureas, and carbamates by repurposing HATU, a common amide coupling reagent. The products are 2-substituted 1,1,3,3-tetramethylguanidines (TMGs), a group of sterically hindered superbases. The reaction of a guanidinium salt with aliphatic amines has been regarded as an unwanted side-reaction in amide coupling, yet the exact mechanistic details have been unclear. Our mechanistic investigation shows that the guanylation is highly dependent on the nature of the nitrogen nucleophile. Our findings were applied on two fronts: minimizing guanylation in competing amide coupling reactions as well as maximizing guanylation in a simple one-step synthesis of a broad variety of 2-substituted TMGs, including the late-stage functionalization of pharmaceuticals.

80 Choline Oxidase and Choline Ionic Liquids in Biocatalytic Heme Peroxidase Cascades
M. Hallamaa, J.M. Naapuri, R.A.L. Silva, A.A. Rosatella J. Deska, ChemCatChem, 2025, 17, e202401216
Choline-derived ionic liquids serve as both solubilizing additives and reagents in a series of synthetic-organic transformations with heme peroxidases as biocatalysts. Choline oxidase from Alcaligenes sp. complements the bi-enzymatic reaction systems in providing H2O2 in situ from air and choline. This study demonstrates the general applicability alongside certain limitations of choline-fueled peroxidase catalysis in halogenations, oxygenations, and dehydrogenations, rendering a variety of O- and N-heterocyclic building blocks.

79 A Sustainable Approach to Cantharellus cibarius oil Through Supercritical Fluid Extraction
A. Ray, S. Nardjes, A. Bashein, J. Deska, A. Sharma, R. S. Singhal, S. S. Shamekh, ACS Food Sci. Technol. 2025, under revision
Cantharellus cibarius, sometimes known as the "boreal chanterelle," is a member of the phylum Basidiomycota and one of the most sought edible mushrooms in the world. This study compared the use of supercritical fluid extraction (SFE), which is regarded as a mild and green extraction method, with the traditional solvent extraction to obtain C. cibarius oils. The optimized parameters of the SFE were obtained through a Box-Behnken design and the SFE approach provided oil yields that exceeded conventional extraction yields with ethyl acetate (10.1 % w/w vs 8.1 % w/w) while exhibiting better selectivity for the accumulation of lipophilic bioactives. Most importantly, the supercritically extracted oil showed significant radical scavenging activities (65% inhibition against ABTS, compared to 58% in the conventionally ethyl acetate-extracted oil), antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, as well as bactericidal effects against Bacillus cereus, Escherichia coli, and Salmonella typhi. The C. cibarius oils extracted through a green technology could be a potential application as condiment with retained bioactive properties.
2024
78 Realities of the consortium approach in science: sustainable enzymatic production of C1 chemicals from carbon dioxide
A. Rodil, I. von Ossowski, M. Nyyssönen, Y. Tian, M. Hallamaa, J. Deska, M. Bomberg, S. Scheller, RSC Sustainability, 2024, 2, 3264–3275
Research at the frontiers of science is getting increasingly specialised. At the same time, major global challenges require the cooperation and innovation of different research fields. One solution for enhancing scientific discovery and innovation within this landscape is to form research consortia that bring together expertise from different disciplines. Such multidisciplinary efforts are also highly recognized and increasingly enforced by funding agencies. Within this landscape, we established a research consortium consisting of three partners to explore environmental acid-tolerant formate dehydrogenases as novel biocatalysts for formic acid production from CO2. Taking our ambitious project on biocatalytic CO2 valorisation as a case study, we reflect on the realities of forming a research consortium, highlighting some of the related theoretical and technical issues, as well as its intrinsic positive and valuable nourishing effect on researchers. Finally, we offer some constructive criticism and practical advice to other scientists willing to embark on complex scientific projects through collaborations.
2023
77 Multienzymatic Synthesis of γ-Lactam Building Blocks from Unsaturated Esters and Hydroxylamine
C. Jäger, M. Nieger, K. Rissanen, J. Deska, Eur. J. Org. Chem., 2023, 26, e202300288
Nature's way to construct highly complex molecular entities as part of biosynthetic pathways is unmatched by any chemical synthesis. Yet, relying on a cascade of native enzymatic transformations to achieve a certain target structure, biosynthesis is also significantly limited in its scope. In this study, non-natural biocatalytic modules, a peroxidase-mediated Achmatowicz rearrangement and a dehydrogenase-catalyzed borrowing-hydrogen-type isomerization were successfully incorporated into an artificial metabolism, combining the benefits of traditional retrosynthesis with the elegance and efficacy of biosynthetic networks. In a highly streamlined process, the total synthesis of tricyclic angiopterlactone B was achieved in two steps operating entirely in an aqueous environment while relying mainly on enzymes as key reaction mediators.

76 An Artificial In Vitro Metabolism to Angiopterlactone B Inspired by Traditional Retrosynthesis
A. F. Kiefer, Y.-C. Liu, R. Gummerer, C. Jäger, J. Deska, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2023, 62, e202301178

Nature's way to construct highly complex molecular entities as part of biosynthetic pathways is unmatched by any chemical synthesis. Yet, relying on a cascade of native enzymatic transformations to achieve a certain target structure, biosynthesis is also significantly limited in its scope. In this study, non-natural biocatalytic modules, a peroxidase-mediated Achmatowicz rearrangement and a dehydrogenase-catalyzed borrowing-hydrogen-type isomerization were successfully incorporated into an artificial metabolism, combining the benefits of traditional retrosynthesis with the elegance and efficacy of biosynthetic networks. In a highly streamlined process, the total synthesis of tricyclic angiopterlactone B was achieved in two steps operating entirely in an aqueous environment while relying mainly on enzymes as key reaction mediators.
75 Fully Biocatalytic Rearrangement of Furans to Spirolactones
Y.-C. Liu, J.D. Rolfes, J. Björklund, J. Deska, ACS Catal., 2023, 13, 7256−7262
A multienzymatic pathway enables the preparation of optically pure spirolactone building blocks. In a streamlined one-pot reaction cascade, the combination of chloroperoxidase, an oxidase, and an alcohol dehydrogenase renders an efficient reaction cascade for the conversion of hydroxy-functionalized furans to the spirocyclic products. The fully biocatalytic method is successfully employed in the total synthesis of the bioactive natural product (+)-crassalactone D, and as the key module in a chemoenzymatic route yielding lanceolactone A.

74 Aerobic C–N Bond Formation through Enzymatic Nitroso-Ene-Type Reactions
C. Jäger, M. Haase, K. Koschorreck, V. B. Urlacher, J. Deska, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 10.1002/anie.202213671
The biocatalytic oxidation of acylated hydroxylamines enables the direct and selective introduction of nitrogen functionalities via activation of allylic C-H bonds. Utilizing either laccases or an oxidase/peroxidase couple for the formal dehydrogenation of N-hydroxycarbamates and hydroxamic acids with air as terminal oxidant, acylnitroso species are generated under particularly mild aqueous conditions. The reactive intermediates undergo C-N bond formation through an ene-type mechanism and provide high yields both in intramolecular and intermolecular enzymatic aminations. Investigations on different pathways of the two biocatalytic systems and labelling studies provide more insights into this unprecedented promiscuity of classical oxidoreductases as catalysts for nitroso-based transformations.

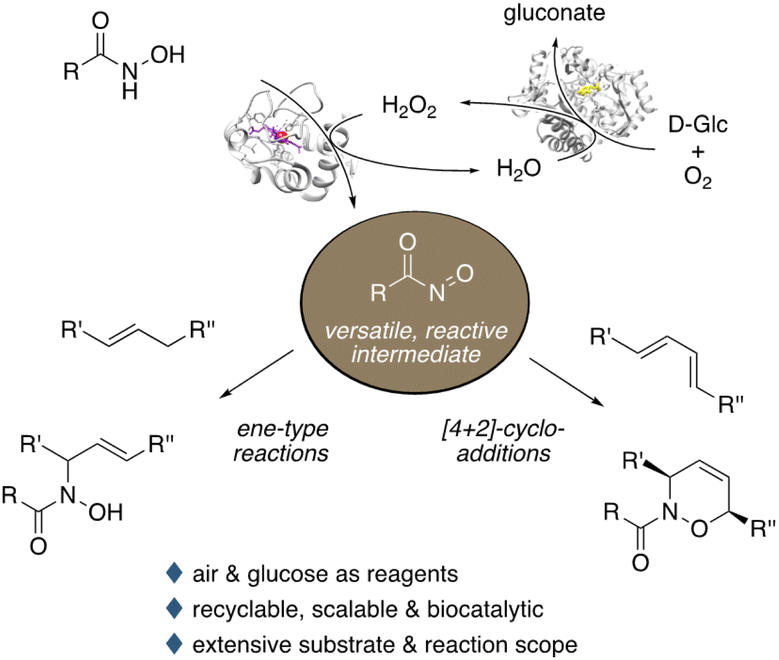
73 Peroxidase-induced C–N bond formation via nitroso ene and Diels–Alder reactions
C. Jäger, B.J. Gregori, J.A.S. Aho, M. Hallamaa, J. Deska, Green Chem., 2023, 25, 3166-3174
The formation of new carbon–nitrogen bonds is indisputably one of the most important tasks in synthetic organic chemistry. Here, nitroso compounds offer a highly interesting reactivity that complements traditional amination strategies, allowing for the introduction of nitrogen functionalities via ene-type reactions or Diels–Alder cycloadditions. In this study, we highlight the potential of horseradish peroxidase as biological mediator for the generation of reactive nitroso species under environmentally benign conditions. Exploiting a non-natural peroxidase reactivity, in combination with glucose oxidase as oxygen-activating biocatalyst, aerobic activation of a broad range of N-hydroxycarbamates and hydroxamic acids is achieved. Thus both intra- and intermolecular nitroso-ene as well as nitroso-Diels–Alder reactions are performed with high efficiency. Relying on a commercial and robust enzyme system, the aqueous catalyst solution can be recycled over numerous reaction cycles without significant loss of activity. Overall, this green and scalable C–N bond-forming strategy enables the production of allylic amides and various N-heterocyclic building blocks utilizing only air and glucose as sacrificial reagents.
72 Coding Synthetic Chemistry Strategies into Bacterial Designer Cells
Y.-C. Liu, Z.-L. Wu, J. Deska, ChemSusChem 2023, 16, e202201790
For the design of a novel functional whole cell tool, two purely abiotic transformations, a styrene monooxygenase-catalyzed Achmatowicz rearrangement and an alcohol dehydrogenase-mediated borrowing hydrogen redox isomerization, were incorporated into a recombinant bacterial host. Introducing this type of chemistry otherwise unknown in biosynthesis, the cellular factories were enabled to produce complex lactone building blocks in good yield from bio-based furan substrates. This whole cell system streamlined the synthetic cascade, eliminated isolation and purification steps, and provided a high degree of stereoselectivity that has so far been elusive in the chemical methodology.

Following a synthetic chemistry blueprint for the valorization of lignocellulosic platform chemicals, this study showcases a so far unprecedented approach to implement non-natural enzyme modules in vivo.
2022
71 Cascade catalysis through bifunctional lipase metal biohybrids for the synthesis of enantioenriched O-heterocycles
from allenes
J. M. Naapuri, N. Losada-Garcia, R. A. Rothemann, M. Carmona Pichardo, M. H. G. Prechtl, J. Palomo, J. Deska, ChemCatChem 2022, 14, e202200362

Hybrid catalysts that provide the reactivity of metal nanoparticles as well as the catalytic performance of their protein support offer new opportunities for the design of novel reaction cascades. In this study, ester hydrolases have been investigated as support for silver and gold Metal nanoparticles are deposited in a polymer-modified protein framework to obtain bifunctional hybrid catalysts that combine the transition metal activities with the host biocatalysts' activation mode. A tailor-made lipase-silver nanobiohybrid is successfully exploited in a cascade design where a racemic allenic acetate is transformed to an enantioenriched dihydrofuran via a sequential hydrolytic kinetic resolution and a cycloisomerization. and the resulting bionanohybrids represent exquisite mediators for the cycloisomerization of allenic alcohols. By merging the transition metal reactivity with the inherent lipase catalysis, allenic acetates are directly converted to the corresponding O-heterocycles in enantiopure form, taking advantage of a kinetic resolution cyclization pathway.
70 Synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles–enzyme–polymer conjugate hybrids as dual-activity catalysts for
chemoenzymatic cascade reactions
J. M. Naapuri, N. Losada-Garcia, J. Deska, J. Palomo, Nanoscale 2022, 14, 5701-5715.
Novel hybrids containing silver or gold nanoparticles have been synthesized in aqueous media and at room temperature using enzymes or tailor–made enzyme–polymer conjugates, which directly induced the formation of inorganic silver or gold species. The choice of pH, protein, or bioconjugate strongly affected the final metallic nanoparticles hybrid formation. Using Candida antarctica lipase (CALB) in a solution, nanobiohybrids containing Ag2O nanoparticles of 9 nm average diameter were obtained. The use of tailor-made bioconjugates, for example, the CALB modified with dextran-aspartic acid polymer (Dext6kDa), resulted in a nanobiohybrid containing smaller Ag(0)/Ag2O nanoparticles. In the case of nanobiohybrids based on gold, Au(0) species were found in all cases. The Au–CALB hybrid contained spherical nanoparticles with 18 nm average diameter size, with a minor range of larger ones (>100 nm) while the AuNPs–CALB–Dext6kDa hybrid was formed by much smaller nanoparticles (9 nm, minor range of 22 nm),

and also nanorods of 20–30/40–50 nm length. Using Thermomyces lanuginosus lipase (TLL), apart from the nanoparticle formation, nanoflowers with a diameter range of 100–200 nm were obtained. All nanobiohybrids maintained (dual) enzymatic and metallic activities. For instance, these nanobiohybrids exhibited exquisite dual-activity for hydrolysis/cycloisomerization cascades starting from allenic acetates. By merging the transition metal reactivity with the inherent lipase catalysis, allenic acetates directly converted to the corresponding O-heterocycles in enantiopure form catalysed by AgNPs–CALB–Dext6kDa, taking advantage of a kinetic resolution/cyclization pathway. These results showed the high applicability of these novel hybrids, offering new opportunities for the design of novel reaction cascades.
69 Enzymatic halocyclization of α- and γ-allenols by chloroperoxidase from Curvularia inaequalis
J. M. Naapuri, P. K. Wagner, F. Hollmann, J. Deska, Chem. Open 2022, 11, e202100236
Vanadate-dependent chloroperoxidase from Curvularia inaequalis catalyzes 5-endo-trig bromocyclizations of α-allenols and 5-exo-trig bromocyclizations of γ-allenols to produce valuable halofunctionalized furans as versatile synthetic building blocks. Benefitting from the vanadate chloroperoxidase's high resiliency towards oxidative conditions, cyclization-inducing reactive hypohalite species are generated in situ from bromide salts and hydrogen peroxide. Crucial requirements for high conversions are aqueous biphasic emulsions as reaction media, stabilized by either cationic or non-ionic surfactants.

2021
68 Beyond hydrophobicity: how F4-TCNQ doping of the hole transport material improves stability of mesoporous triple-cation perovskite solar cells
M. Liu, S. Dahlström, C. Ahläng, S. Wilken, A. Degterev, A. Matuhina, M. Hadadian, M. Markkanen, K. Aitola, A. Kamppinen, J. Deska, O. Mangs, M. Nyman, P. D. Lund, J.-H. Smått, R. Österbacka, P. Vivo J. Mat. Chem. A. 2022, 10, 11721-11731

The oxidative ring expansion of bio-derived furfuryl alcohols to densely functionalized six-membered O-heterocycles represents an attractive strategy in the growing network of valorization routes to synthetic building blocks out of the lignocellulosic biorefinery feed. In this study, two scenarios for the biocatalytic Achmatowicz-type rearrangement using methanol as terminal sacrificial reagent have been evaluated, comparing multienzymatic cascade designs with a photo-bio-coupled activation pathway.
67 Investigation on mycelial growth requirements of Cantharellus cibarius under laboratory conditions
S. Deshaware, S. J. Marathe, D. Bedade, J. Deska, S. Shamekh, Arch. Microbiol. 2021, 10.1007/s00203-020-02142-0
Cantharellus cibarius is one of the most important, wild, edible, ectomycorrhizal (ECM) mushrooms. C. cibarius, popularly known as the golden chanterelle mushroom. This golden chanterelle mushroom has good antioxidant and free radical scavenging activity due to presence of caffeic acid and catechins, has chemo-preventive action. There has been a considerable interest in pigment production by edible mushrooms. During submerged culture for production of bioactive compounds, it has been found that several fungi and edible mushrooms produce pigments with relatively high yield. This study aims to determine the best mycelial growth conditions of C. cibarius for pigment and biomass production under laboratory conditions. Our study provides valuable insight on nutritional requirements of Cantharellus cibarius such as pH, temperature, carbon and nitrogen sources for mycelium growth.
66 In silico characterization of bacterial chitinase: illuminating the evolutionary relationship with archeal and
eukaryotic cousins
B. Datta, J. Deska, R. Bandopadhyay, S. Shamekh
J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2021, 19, 19

Chitin is one of the most abundant biopolymers on Earth, only trailing second after cellulose. The enzyme chitinase is responsible for the degradation of chitin. Chitinases are found to be produced by wide range of organisms ranging from archea to higher plants. Though chitin is a major component of fungal cell walls and invertebrate exoskeleton, bacterialchitinase can be industrially generated at low cost, in facile downstream processes at high production rate.Microbial chitinases are more stable, active and economically practicable compared to the plant and animal derived enzymes. In the present study, we have worked upon the Chitinase, emphasizing of bacterial origin which is fulfilling all the required quality needed to be a commercial production. 62 Chitinase sequences from four different group of organisms are collected from RCSB PDB. Considering one suitable sequence from each group is being compared with others. Primary, secondary and tertiary structures are determined by in silicomodels. Different physical parameters viz., pI, molecular weight, instability index, aliphatic index, GRAVY, presence of functional motifs are determined. Phylogenetic tree has been constructed to find out the relationship with other group of organisms. These provides insight into distribution of chitinase and further characterization and industrial assessment of the desired enzyme.
2020
67 Arylative Allene Cyclization by Sequential Enzyme & Palladium Catalysis
J. M. Naapuri, G. A. Åberg, J. M. Palomo, J. Deska,
ChemCatChem 2020, 13, 763-769.

The one-pot combination of halogenation biocatalysis and Suzuki-type cross coupling enables the direct arylative cyclization of allenic alcohols with boronic acids. This modular approach to unsaturated five-membered O-heterocycles proceeds in an aqueous emulsion with air as terminal oxidant. Here, the enzymatic oxidative activation of simple halide salts acts as traceless ring-closure-inducing event to trigger the subsequent C‑C coupling. With the original protocol merging soluble proteins and a homogeneous SPhos-based palladium catalyst as a template, a novel heterogeneous nanobiohybrid was developed. Consisting of an oxidase matrix hosting small spherical palladium nanoparticles, this enzyme-metal hybrid exhibits catalytic competence for both the biocyclization as well as the C‑C bond-forming cross coupling, underlining the potential of this new techniques for streamlining chemoenzymatic approaches.
66 Anti-angiogenic and anti-inflammatory activity of the truffle 'Tuber aestivum' extracts and a correlation with the chemical constituents identified therein
S. J. Marathe, W. Hamzi, A. M. Bashein, J. Deska, T. Seppänen-Laakso, R S. Singhal, S. Shamekh
Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109699
Fungi are a very rich source of untouched bioactive compounds. Owing to their biological activities, several fungi have shown commercial application in the health industry. Tuber aestivum is one such fungi with an immense potential for practical biological application. In the present study, the anti-angiogenic activity of petroleum ether and ethanol extracts of T. aestivum was investigated using the chick chorioallantoic membrane assay and compared to the positive controls silibinin and lenalidomide. Both extracts showed a dose-dependent anti-angiogenic response. The extracts were also assessed for their anti-inflammatory potential through a lipoxygenase-inhibition assay. The IC50 values in LOX inhibition assay, computed by the Boltzmann plot, were 368.5, 147.3 and 40.2 µg/mL, for the petroleum ether, ethanol extracts, and the positive control ascorbic acid, respectively. In direct comparison, the ethanol extract of T. aestivum showed superior anti-angiogenic and anti-inflammatory activity than the petroleum ether extract. Compositional investigation of the extracts was performed using GC-MS analysis and revealed the presence of various bioactive compounds. The compounds were correlated to their anti-angiogenic and anti-inflammatory activity based on a meticulous literature search.
2019
65 Biocatalytic production of amino-carbohydrates through oxidoreductase and transaminase cascades
V. Aumala, F. Mollerup, E. Jurak, F. Blume, J. Karppi, A. E. Koistinen, E. Schuiten, M. Voß, U. T. Bornscheuer, J. Deska, E. R. Master
ChemSusChem 2019, 12, 848-857
Plant-derived carbohydrates constitute an abundant renewable resource. Transformation of carbohydrates into new products, including amine-functionalized building blocks for biomaterial applications, can lower reliance on fossil resources. Herein, we demonstrate biocatalytic production routes to amino-carbohydrates, including oligosaccharides. In each case, we performed a two-step biocatalysis to functionalized D-galactose-containing carbohydrates, which employed either the galactose oxidase from Fusarium graminearum or a pyranose dehydrogenase from Agaricus bisporus followed by the w-transaminase from Chromobacterium violaceum (Cvi-w-TA). Formation of 6-amino-6-deoxy-d-galactose, 2-amino-2-deoxy-d-galactose and 2-amino-2-deoxy-6-aldo-d-galactose

was confirmed by mass spectrometry. Cvi-w-TA activity was highest towards 6-aldo-d-galactose and xyloglucan oligosaccharides, where highest yield of 6-amino-6-deoxy-d-galactose from d-galactose (60%) was achieved in reactions permitting simultaneous oxidation of d-galactose and transamination of the resulting 6-aldo-d-galactose. .
64 Chemoenzymatic Hydrogen Production from Methanol Through the Interplay of Metal Complexes and Biocatalysts
G. Tavakoli, J. E. Armstrong, J. M. Naapuri, J. Deska*, M. H. G. Prechtl*, Chem. Eur. J. 2019, 25, 6474-6481

Bacterial methylotrophic organisms can serve as great inspiration in the development of biomimetic interconversion of C1 molecules at ambient conditions. In this concept article, we give a brief personal perspective on the recent advancement in the field of biomimetic catalytic interconversion of methanol and formaldehyde in presence and absence of enzymes and co-factors towards the formation of hydrogen at ambient conditions. In particular organometallic formaldehyde dehydrogenase and dismutase mimics have been introduced in standalone C1-interconversion networks. Also, coupled systems with alcohol oxidase and dehydrogenase enzymes for the in situ formation and decomposition of formaldehyde and/or NADH/NAD+ have been developed in recent years. These conceptual bio-inspired low-temperature energy conversion processes may lead one day to more efficient energy storage systems enabling hydrogen generation for hydrogen fuel cells at ambient conditions using C1 molecules as fuels.
63 Shape and Phase Transitions in a PEGylated Phospholipid System
L. Viitala, S. Pajari, L. Gentile, J. Määttä, M. Gubitosi, J. Deska, M. Sammalkorpi, U. Olsson, L. Murtomäki
Langmuir 2019, 35, 3999-4010

Poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) polymers and PEG-conjugated lipids are widely used in bioengineering and drug transport applications. The PEG layer increases hydrophilic repulsion, inhibits membrane fusion and serum opsonin interactions, and prolongs the storage and circulation times, but it can also change the carrier shape and have influence to many content-release-related properties. In this paper, we focus on the physicochemical effects of PEGylation in the lipid bilayer. We use cryo-TEM, DSC, molecular dynamics (MD) simulations, fluorescence spectroscopy of laurdanC, and SAXS/WAXS to acquire information of the particle/bilayer morphology and phase behavior in systems containing DPPC:DSPE-PEG(2000) with different fractions. We show that there are two regions of interest that could be used to improve PEGylated lipid applications. The first one involves spherical vesicles and a window of elevated chain melting temperatures that could be utilized in targets requiring multiple release sequences. The other region is the liposome-to-bicelle transition that is indirectly controlled by the polymer size. This important finding could be used to achieve more efficient drug release and to control other smart materials.
2018
Alcohol dehydrogenases can act as powerful catalysts in the preparation of optically pure gamma-hydroxy-delta-lactones by means of an enantioconvergent dynamic redoxisomerization of readily available Achmatowicz-type pyranones. Imitating the traditionally metal-mediated borrowing hydrogen approach to shuffle hydrides across molecular architectures and interconvert functional groups, this chemoinspired and purely biocatalytic interpretation effectively expands the enzymatic toolbox and provides new opportunities in the assembly of multi-enzyme cascades and tailor-made cellular factories.
62 Biocatalytic Enantioconvergent Redoxisomerization
Y.-C. Liu, C. Merten, J. Deska,
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 12151-12156
Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 12328-12333
61 Kirmse-Doyle- and Stevens-type Rearrangements of Glutarate-derived Oxonium Ylides
B. Skrobo, N. E. Schlörer, J.-M. Neudörfl, J. Deska
Chem. Eur. J. 2018, 24, 3209-3217

A novel chemoenzymatic synthetic cascade enables the preparation of densely decorated tetrahydrofuran building blocks. Here, the lipase-catalyzed desymmetrization of 3-alkoxyglutarates renders highly enantioenriched carboxylic acid intermediates, whose subsequent activation and oxonium ylide rearrangement by means of rhodium or copper complexes furnishes functionalized O-heterocycles with excellent diastereoselectivity. The two-step protocol offers a streamlined and flexible synthesis of tetrahydrofuranones bearing different benzylic, allylic or allenylic side chains with full control over up to three stereogenic centers.
60 Chloroperoxidase-catalyzed Achmatowicz Rearrangements
D. Thiel, F. Blume, C. Jäger, J. Deska
Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 20, 2717-2725.

Chloroperoxidase from Caldariomyces fumago catalyzes the selective oxidation of furfuryl alcohols in an Achmatowicz-type ring expansion. In combination with glucose oxidase as oxygen-activating biocatalyst, a purely enzymatic, aerobic protocol for the synthesis of 6-hydroxypyranone building blocks is obtained. Thanks to an only modest stereochemical bias of the oxygenating heme protein, optically active alcohols of either configuration are converted without a significant mismatch opening up opportunities for enantioselective multienzymatic cascades. Balancing the oxidase-driven aerobic activation, extended enzyme half-lifes and productive conversion of poorly soluble and slowly reacting substrates can be achieved with high yields of the six-membered O‑heterocycles.
59 Lipase-induced Oxidative Furan Rearrangements
F. Blume, P. Sprengart, J. Deska
Synlett 2018, 29, 1293-1296

Lipase B from Candida antarctica catalyzes the oxidative ring expansion of furfuryl alcohols using aqueous hydrogen peroxide to yield functionalized pyranones under mild conditions. The method further allows for the preparation of corresponding piperidinone architectures by enzymatic rearrangement of N-protected furfurylamines.
58 Fermentative production of extracellular amylase from novel amylase producer, Tuber maculatum mycelium
D. K. Bedade, R. S. Singhal, S. Bankar, S. Bejar, J. Deska, S. Shamekh
Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2018, 48, doi: 10.1080/10826068.2018.1478976
Truffles are symbiotic hypogeous edible fungi that form filamentous mycelia in their initial phase of the growth cycle as well as a symbiotic association with host plant roots. In this study, Tuber maculatum mycelia were isolated and tested for extracellular amylase production at different pH on solid agar medium. Furthermore, the mycelium was subjected to submerged fermentation for amylase production under different culture conditions such as variable carbon sources and their concentrations, initial medium pH, and incubation time. The optimized conditions after the experiments included soluble starch (0.5% w/v), initial medium pH of 7.0, and incubation time of 7 days, at room temperature (22 ± 2 °C) under static conditions which resulted in 1.40 U/mL of amylase. The amylase thus obtained was further characterized for its biocatalytic properties and found to have an optimum activity at pH 5.0 and at a temperature of 50 °C. The enzyme showed good thermostability at 50 °C by retaining 98 % of the maximal activity after 100 min of incubation. The amylase's performance was enhanced in presence of Cu2+ additives and slightly reduced by K+, Ca2+, Fe2+, Mg2+, Co2+, Zn2+, and Mn2+ ions at 1 mM concentration.
2017
57 Enzymatic Halocyclization of Allenic Alcohols & Carboxylates: A Biocatalytic Entry to Functionalized O-Heterocycles
J. Naapuri, J. D. Rolfes, J. Keil, C. Manzuna Sapu, J. Deska
Green Chem. 2017, 19, 447-452.

Chloroperoxidase from Caldariomyces fumago catalyzes the aerobic oxidative halocyclization of allenic alcohols and carboxylates yielding functionalized furan and pyran heterocycles as valuable synthetic scaffolds. Thanks to an oxidase-initiated redox cascade, simple halide salts – in combination with air and glucose – act as stoichiometric reagents for the in situ generation of reactive halonium species. Under the mild reaction conditions in an aqueous emulsion medium, the stereochemical integrity of diastereo- and enantioenriched allenes remains uncompromised and chiral dihydrofurans can be obtained via 5-endo-trig cyclizations with perfect axis-to-centre chirality transfer.
56 Extracellular Xylanase Production from a New Xylanase Producer Tuber maculatum Mycelium under Submerged Fermentation and its Characterization
D. K. Bedade, O. Berezina, R. Singhal, J. Deska, S. Shamekh
Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2017, 11, 288-293.
Truffles are edible fungi that grow symbiotically with several trees. In this study, Tuber maculatum mycelia were isolated and screen qualitatively for extracellular xylanase production at a broad pH range (4.0, 7.0 and 9.0) in agar plates. Based on zone of clearance highest xylanase activity was observed at pH 7.0. Furthermore, T. maculatum mycelium was studied for effect of various carbon sources, initial medium pH, agitation and fermentation time on xylanase production in submerged fermentation. Under optimized conditions maximum xylanase activity (13.15 U/mL) was detected after 6 days of fermentation at static condition in the basal salt medium with the initial medium pH of 7.0 and 0.5% xylan. The xylanase showed maximum activity at 50 °C and pH 5.0. The Zn2+ activated the xylanase but Co2+ was found inhibitory towards the same. The results indicated that truffle mycelium is utilizing xylan as energy source from host plant root system.
55 Biochemical Characterization of Extracellular Cellulase from Tuber maculatum mycelium produced under submerged fermentation
D. K. Bedade, O. Turunen, J. Deska, S. Shamekh
Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2017, 181, 772-783.
Interaction of truffle mycelium with the host plant involves the excretion of extracellular enzymes. Tuber maculatum mycelia were isolated and tested for extracellular cellulase production at variable pH (4.0, 7.0 & 9.0) on solid agar medium, and the highest activity was observed at pH 7.0. Furthermore, T. maculatum was subjected to submerged fermentation in basal salt medium for cellulase production. Under optimized conditions using sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (0.5% w/v) as carbon source and an initial pH of 7.0, the enzyme production yielded 1.70 U/ml of cellulase in the cell-free cultural liquid after seven days of incubation time. The optimum of the obtained cellulase's activity was at pH 5.0 and a temperature of 50 °C. The enzyme showed good thermostability at 50 °C by retaining 99 % of its maximal activity over an icubation time of 100 min. The cellulase activity was inhibited by Fe2+ and slightly activated by Mn2+ and Cu2+ at 1 mM concentration. The results indicated that truffle mycelium is utilizing cellulosic energy source in the root system and the optimal conditions are those existing in the acidic Finnish soil.
2016
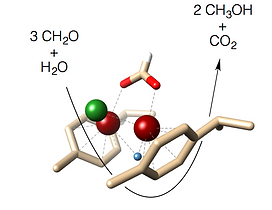
54 An Organometallic Dismutase – Self-Sufficient Formaldehyde-to-Methanol Conversion
D. van der Waals, L. E. Heim, S. Vallazza, C. Gedig, J. Deska, M. H. G. Prechtl
Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 11568-11573.
The catalytic networks of methylotrophic organisms featuring redox enzymes for the activation of one-carbon moieties can serve as great inspiration in the development of novel homogeneously catalysed pathways for the interconversion of C1 molecules at ambient conditions. An imidazolium-tagged arene-ruthenium complex was identified as an effective functional mimic of bacterial formaldehyde dismutase that provides a novel and highly selective route for the conversion of formaldehyde to methanol in absence of any external reducing agents. Moreover, secondary amines are reductively methylated by the organometallic dismutase mimic in a redox self-sufficient manner with formaldehyde acting both as carbon source and reducing agent.
53 Chemoenzymatic Total Synthesis of (+)- & (−)-cis-Osmundalactone
F. Blume, Y. C. Liu, D. Thiel, J. Deska
J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2016, 134, 280-284.

Both optical antipodes of the cis-isomers of osmundalactone, a hydroxypyranone natural product and core structure of the angiopterlactones, have been synthesized from acetylfuran in only three steps through a redox cascade utilizing oxidoreductases and transition metal catalysis in a concerted fashion. The key step in this fully catalytic strategy is the enzyme-mediated Achmatowicz reaction via selective furan oxygenation to furnish the pyran core structure.
52 Enzymatic Approaches for the Preparation of Optically Active Non-Centrochiral Compounds
B. Skrobo, J. D. Rolfes, J. Deska
Tetrahedron. 2016, 72, 1257-1275. Link

This report provides a full summary over all activites exploiting biocatalysis for the synthesis of enantioenriched axially, planarly, and helically chiral molecules over the past four decades. Introducing the basic activation modes of the most frequently employed enzyme classes, this review will highlight the power of biocatalysis – ranging from classical whole-cell systems to contemporary tailor-made proteins – to effectively act on highly non-natural substrate structures in a synthetic fashion.
2015
51 Bioinduced Room Temperature Methanol Reforming
L. E. Heim, D. Thiel, C. Gedig, J. Deska,* M. H. G. Prechtl*
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 10308-10312, Link; Angew. Chem. 2015, 127, 10447-10451, Link. Hot Paper
Imitating Nature's approach in nucleophile-activated formaldehyde dehydrogenation, air stable ruthenium complexes proved to be exquisite catalysts for the dehydrogenation of formaldehyde hydrate as well as for the transfer hydrogenation to unsaturated organic substrates at loadings as low as 0.5 mol%. Concatenation of the chemical hydrogen fixation route with an oxidase-mediated activation of methanol renders an artificial methylotrophic in vitro metabolism providing methanol-derived reduction equivalents for synthetic hydrogenation purposes. Moreover, for the first time methanol reforming at room temperature was achieved on the basis of this bioinduced dehydrogenation path delivering hydrogen gas from aqueous methanol.

50 The Achmatowicz Rearrangement: Oxidative Ring Expansion of Furfuryl Alcohols (review)
J. Deska, D. Thiel, E. Gianolio
Synthesis 2015, 47, 3435-3450. Link

Over the years, the oxidative ring enlargement of furfuryl alcohols, known as Achmatowicz reaction, has been developed to a powerful and versatile synthetic tool for the preparation of 6-hydroxypyranones. This review provides a comprehensive collection of the various ways to perform Achmatowicz rearrangement reactions and explores the role of this ring expansion process in contemporary organic synthesis.
49 Alkylative Amination of Biogenic Furans via Imine-to-Azaallyl Umpolung
F. Blume, M. H. Albeiruty, J. Deska
Synthesis 2015, 47, 2093-2099. Link

Starting from biogenic furfurals, an operationally simple and scalable condensation-umpolung-alkylation protocol was employed in the synthesis of racemic furfurylamines. Subsequent enzymatic kinetic resolution by ω-transaminase or lipase biocatalysts allows for the preparation of functionalized heterocyclic building blocks from biogenic base chemicals in optically pure form.
2014
48 Enzymatic Aerobic Rearrangement of Optically Active Furylcarbinols
D. Thiel, D. Doknic, J. Deska
Nature Commun. 2014, 5, 5278. Link

Biogenic furans are currently discussed as highly attractive alternative feedstock in a post-fossil society; thus, also the creation of sustainable furan valorization pathways appears of great importance. Here an artificial Achmatowicz monooxygenase activity for the aerobic ring expansion of furans is achieved by the combination of commercial glucose oxidase as oxygen-activating biocatalyst and wild-type chloroperoxidase as oxygen-transfer mediator, providing a biological ready-to-use solution for this truly synthetic furan rearrangement. In concert with enzymatic transformations for the enantioselective preparation of optically active furylcarbinols, purely biocatalytic reaction cascades for the stereocontrolled construction of complex pyranones are obtained, exhibiting high functional group tolerance even to oxidation-sensitive moieties.
47 Migratory Dynamic Kinetic Resolution of Carbocyclic Allylic Alcohols
C. Manzuna Sapu, T. Görbe, R. Lihammar, J.-E. Bäckvall, J. Deska*
Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 5952-5955. Link
A novel migratory dynamic kinetic resolution based on the interplay between an enzyme acylation catalyst and a heterogeneous Brønsted acid as an isomerization/racemization catalyst gives rise to carbocyclic allylic esters with excellent stereoselectivity from readily available tertiary carbinols. An easy-to-use teabag setup combining resin-bound catalysts, a biphasic isooctane–water solvent system, and a highly lipophilic acyl donor efficiently suppresses side reactions and allows for the preparation of functionalized carbocyclic building blocks in high yields and optical purity.

2013
46 Oxonium Ylide Rearrangement of Enzymatically Desymmetrized Glutarates
B. Skrobo, J. Deska
Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 5998-6001. Link

The combination of an enzyme-mediated enantioselective desymmetrization of readily available 3-benzyloxy-glutarates and subsequent rhodium-catalyzed oxonium ylide rearrangement of their corresponding in situ derived diazo ketones offers a very concise and highly stereoselective access to functionalized tetrahydro-furanone building blocks.
45 Chemoenzymatic Total Synthesis of Hyperiones A & B
C. Manzuna Sapu, J. Deska
Org. Biomol. Chem. 2013, 11, 1376-1382. Link
The first asymmetric total synthesis of hyperiones A and B, two norlignans from Hypericum chinense, has been accomplished following a chemoenzymatic approach. Key features of this synthesis include the lipase-catalyzed enantioselective desymmetrization of a prochiral allenic diol and a silver-mediated cycloisomerization of the resulting axially chiral product to furnish the furan core structure. Two alternative pathways, a ruthenium-catalyzed redox isomerization on the one side and a platinum-catalyzed hydrogenation on the other, are described to finally obtain the desired norlignans.

44 Modular Synthesis of Optically Active Tröger's Base Analogues
T. Kamiyama, M. S. Özer, E. Otth, J. Deska, J. Cvengros
ChemPlusChem 2013, 78, 1510-1516. Link

For the first time, enantioselective catalysis was applied for the preparation of Tröger's base derivatives affording N-stereogenic building blocks not only in excellent enantiomeric purity but also in an easily scalable fashion. Enzymatic kinetic resolution proved efficient to yield functionalized Tröger's bases, which can be subsequently modified by various chemical methods without any erosion of stereogenic information.
43 On a Chemoenzymatic Desymmetrization/Ring Expansion Strategy towards Functionalized N-Heterocycles
D. Thiel, J. Deska
Synlett 2013, 24, 1529-1532. Link
The direct combination of the desymmetrization of N-hetero-cyclic meso-diols using lipase from Mucor miehei as biocatalyst and subsequent ring expansion of the optically active products by activation of the remaining hydroxy group gives rise to functionalized nonsymmetrical piperidines in a highly enantio- and diastereoselective manner.

42 On the Lipase-catalyzed Resolution of Functionalized Biaryls
B. Skrobo, J. Deska
Tetrahedron: Asymmetry 2013, 24, 1052-1056. Link

The implementation of lipase catalysis as a tool for the preparation of optically active biaryls is discussed. While attempts toward dynamic kinetic resolution based on the catalytic ring opening of configurationally unstable biaryl lactones were fruitless, kinetic resolution via transesterification of hydroxymethyl-decorated substrates was successfully employed in the generation of optically enriched, axially chiral biaryls.
41 Palladium-catalyzed Allylic Alkylation as Versatile Tool in Amino Acid and Peptide Modifications
U. Kazmaier, A. Bayer, J. Deska
Synthesis 2013, 45, 1462-1468. Link

Palladium-catalyzed allylic alkylations are especially suitable for the introduction of γ,δ-unsaturated side chains into amino acids and even peptides. Glycine ester enolates are generally used as nucleophiles in these reactions, they react at a very low temperature (–78 °C) to give the products of isomerization-free allylation. In reactions of cis-configured allylic substrates, the olefin geometry can be transferred to the product. Because the syn position of the corresponding syn/anti π-allyl complex formed in this case is more reactive, this isomerization-free protocol also allows regioselective and stereoselective allylations. Using stannylated allylic substrates gives metalated amino acid derivatives that are ideal substrates for subsequent Stille couplings or tin–iodine exchange reactions. If peptides are deprotonated with excess strong base, the corresponding ester or amide enolates formed can also be subjected to allylation; in this case the stereochemical outcome can be controlled by the peptide chain.
2012
40 Enantioselective Synthesis of Axially Chiral Tetrasubstituted Allenes via Lipase-catalyzed Desymmetrization
M. Hammel, J. Deska
Synthesis 2012, 44, 3789-3796. Link
Lipase from Pseudomonas fluorescens efficiently catalyzes the transesterification of prochiral tetrasubstituted allenic diols yielding highly enantioenriched axially chiral allenyl monoesters. In combination with subsequent 5-endo-trig cyclizations geminally disubstituted dihydrofurans are accessible in high optical purity.

2011
39 Enantioselective Enzymatic Desymmetrization of Prochiral Allenic Diols
C. Manzuna Sapu, J.-E. Bäckvall, J. Deska
Angew. Chem. 2010, 123, 9905-9908; Link, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 9731-9734. Link

Crude lipase from porcine pancreas acts as a highly efficient biocatalyst in the enantioselective transesterification of prochiral allendiols. Following a simple synthetic protocol, highly functionalized axially chiral allenes are obtained in high yields and excellent enantiopurity
38 Stereoselective Synthesis of Deuterated b-Cyclohexenylserine, a Biosynthetic Intermediate of the Salinosporamides
J. Deska, S. Hähn, U. Kazmaier
Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 3210-3213. Link

A straightforward, highly stereoselective protocol toward the synthesis of deuterium-labeled (2R,3S,4S)-β-cyclohexenylserine has been developed. Key steps are a Nozaki–Hiyama–Kishi reaction generating the stereogenic centers and a ring-closing metathesis for the construction of the cyclohexenyl ring system. The labeled amino acid was further activated as an SNAc-ester for feeding experiments.
2006 - 2010

